Do you want to learn how to play your favorite songs by ear? Do you want to improve your musical ear, memory, and creativity? Do you want to have fun and challenge yourself with music?
If you answered yes to any of these questions, then you need to learn how to transcribe music by ear.
Transcribing music by ear is a skill that involves listening to a piece of music and identifying the notes, chords, rhythms, and other musical elements by using your ears and an instrument. It can help you develop your musical abilities and enjoy music more.
But how do you transcribe music by ear? What do you need to know and do? How do you start and progress?
In this guide, we will show you how to transcribe music by ear step by step. By the end of this guide, you will be able to transcribe any piece of music that you want by ear.
If you want to transcribe audio, extract audio from video, or generate text to speech with realistic or funny voices, try FineShare FineVoice. This real-time voice changer for PC meets your needs.
Before we dive into the details and examples of how to transcribe music by ear, let’s first review some general strategies that can help you transcribe music more easily and effectively. These are:
General Strategies for Transcribing Music
#1. Use your ears and musical knowledge to transcribe music, not just your eyes and fingers. This can help you develop your musical ear, memory, and creativity, as well as your playing skills and confidence.
#2. Use different tools and methods to transcribe music, not just one. This can help you save time and effort, as well as provide you with accurate and reliable results.
You can use software or apps that can slow down the music, change the key, and automatically identify notes and chords (For example, Audacity or Transcribe!). You can also use paper and pen that you can use to write down your transcription using traditional notation symbols.
#3. Use other sources to verify and improve your transcription, not just your own. This can help you confirm or correct your transcription, as well as discover new insights or perspectives on the piece. You can use sheet music, online tutorials, or other transcriptions that are related to your piece.
#4. Use sheet music, online tutorials, or other transcriptions that are related to your piece and see how they compare with yours. You can also use research papers, articles, books, videos, podcasts, etc., that can provide more information or evidence for your points or claims.
#5. Divide the music into several parts and transcribe them one by one. This can help you focus on specific parts of the piece and not get overwhelmed by the whole piece. You can divide the music into sections, such as the intro, verse, chorus, bridge, etc., and transcribe them in order.
What You Need to Transcribe Music by Ear
To transcribe music by ear, you need:
#1. A good sense of pitch and harmony. Pitch is the highness or lowness of a sound. Harmony is the combination of notes or chords that create a pleasing or interesting sound. You need to be able to hear and recognize different pitches and harmonies in music.
#2. An instrument that you can play along with the music and find the pitches and chords. You can use any instrument that you are comfortable with, but some instruments are more suitable for transcribing than others. For example, a piano or a guitar can help you visualize the notes and chords better than a violin or a flute.
#3. A device that allows you to pause, rewind, fast-forward, slow down, loop, or change the pitch of the music. This can help you focus on specific parts of the piece and make them easier to hear and play. You can use a CD player, a computer, a smartphone, or an app for this purpose
#4. A piece of music that you want to transcribe. It can be any genre or style that you like, but it should be within your skill level and not too complex or fast.

How to Transcribe Music by Ear Step by Step
To transcribe music by ear, you need to follow these steps:
Step 1: Choose a Piece of Music
The first step is to choose a piece of music that you want to transcribe. It can be any genre or style that you like, but it should be within your skill level and not too complex or fast.
You can choose a piece of music that you already know and like, or a piece of music that you are curious about and want to learn. You can also choose a piece of music that has some features that interest you, such as a catchy melody, a cool chord progression, a funky rhythm, etc.
If it’s the first time you transcribe music by ear, I can recommend a piece of music for you. Here are some criteria and examples of pieces of music that are suitable for beginners:
- The piece of music should have a simple and clear melody that is easy to sing or hum along with the music. For example, you can try transcribing “Happy Birthday”, “Twinkle Twinkle Little Star”, “Amazing Grace”, or any other familiar song that you know and like.
- The piece of music should have a simple and consistent harmony that is easy to identify and play along with the melody. For example, you can try transcribing “Stand by Me” by Ben E. King, “Let It Be” by The Beatles, “Wonderwall” by Oasis, or any other song that uses basic chords and progressions that you know and like.
- The piece of music should have a simple and steady rhythm that is easy to tap or clap along with the music. For example, you can try transcribing “We Will Rock You” by Queen, “Eye of the Tiger” by Survivor, “Billie Jean” by Michael Jackson, or any other song that has a strong and regular beat that you know and like.
Step 2: Listen to the Piece of Music
The second step is to listen to the piece of music several times and get familiar with it. Use headphones or earphones to listen to the music. This can help you block out any background noise and hear the music more clearly and closely.
And listen to the music actively and attentively. This means that you should not just listen to the music passively or casually, but try to analyze and understand what is happening in the music and how it is affecting you.
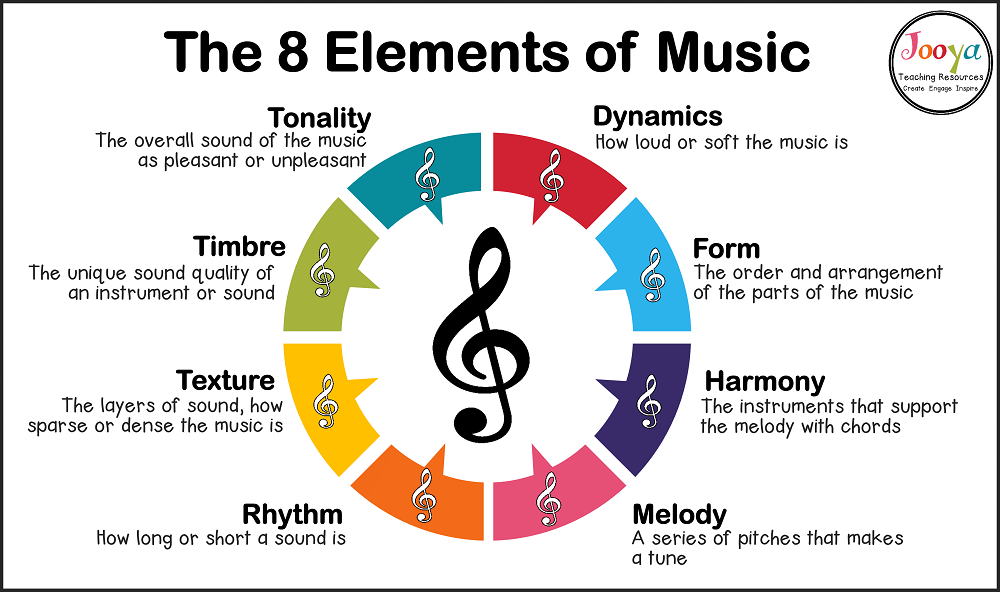
You need to pay attention to the different musical elements and aspects of the piece, such as:
- The melody (the main tune or theme that is usually sung or played by the lead instrument or voice)
- The harmony (the combination of notes or chords that support or accompany the melody)
- The rhythm (the pattern of beats and accents that give the piece its groove and feel)
- The key signature (the sharps or flats at the beginning of each staff line that indicate which notes are higher or lower than usual)
- The time signature (the numbers at the beginning of each staff line that indicate how many beats are in each measure and what kind of note gets one beat)
- The tempo (the speed of the music)
- The form (the structure or arrangement of the sections)
Step 3: Transcribe the Melody
The third step is to transcribe the melody. The melody is usually the most prominent and recognizable part of the piece. It is also the part that you will probably remember and sing or hum along with the music.
Listen to it carefully and try to sing or hum it along with the music. Play it on your instrument by finding the notes that match your voice. Use a tuner or a reference note (such as a middle C) to help you find the right pitch.
Recommended techniques: solfege, or intervals.

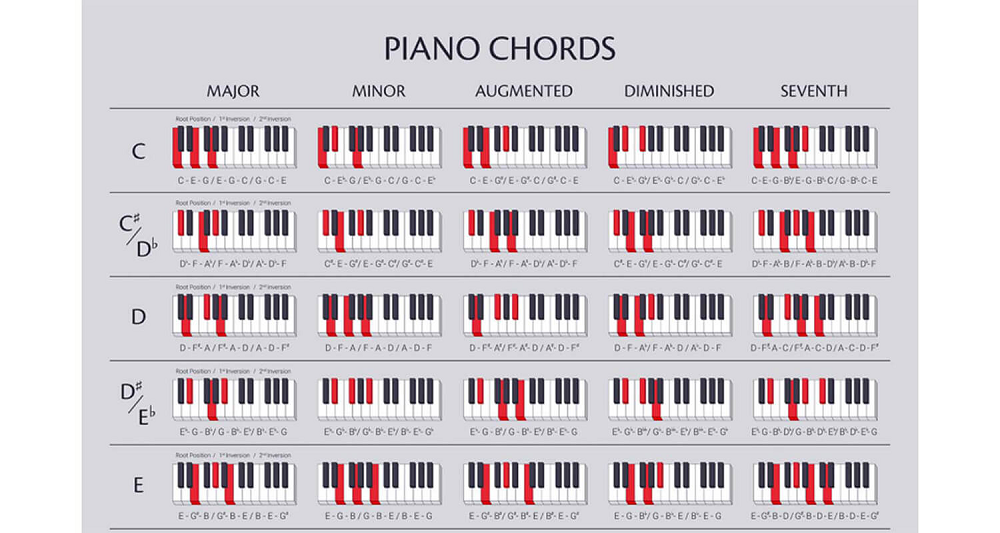
Step 4: Transcribe the Harmony
The fourth step is to transcribe the harmony. The harmony is usually created by the chords that accompany the melody. It is also the part that gives the piece its mood and emotion.
Listen to it carefully and try to identify the chord tones (the notes that make up each chord) that support the melody notes.
Recommended techniques: chord formulas or patterns
Step 5: Transcribe the Rhythm
The fifth step is to transcribe the rhythm. The rhythm is usually created by the beats and accents that give the piece its groove and feel. It is also the part that determines how long each note or chord lasts.
Listen to it carefully and try to tap or clap it along with the music. Use a metronome or a reference beat (such as a quarter note) to help you find the right tempo. Then, play it on your instrument by finding the note values and durations that match your taps or claps.
Recommended techniques: counting or subdividing (breaking down each beat into smaller parts)
Step 6: Repeat These Steps for Each Section of the Piece
The sixth step is to repeat these steps for each section of the piece until you have transcribed the whole piece. You need to identify the main sections of the piece, such as the intro, verse, chorus, bridge, etc., and transcribe them one by one.
Step 7: Check Your Transcription Against the Original Piece
The seventh step is to check your transcription against the original piece and correct any mistakes or inaccuracies. You need to listen to the original piece and compare it with your transcription and see if they match or not.
How to Practice and Improve Your Transcription Skills
To practice and improve your transcription skills, you need to:
#1. Transcribe music regularly and consistently. This can help you develop your musical ear, memory, and creativity, as well as your playing skills and confidence.
#2. Transcribe different types of music. This can help you expand your musical repertoire, knowledge, and taste, as well as challenge yourself with new genres, styles, and techniques.
#3. Transcribe music that you enjoy and are passionate about. This can help you have fun and stay motivated with music.
#4. Transcribe music with others. This can help you share your musical ideas, experiences, and feedback with other musicians, as well as learn from them.

Conclusion
Transcribing music by ear is a valuable skill for any musician to learn, as it can improve your listening, playing, and writing abilities. But it can also be challenging and time-consuming, so it requires patience and practice.
In this guide, we have shown you how to transcribe music by ear step by step. We have also given you strategies and tips. By the way, FineShare FineVoice unleashes the charm of your voice. Try this AI digital voice solution for free!
FAQ
#1. What does it mean to transcribe music?
Transcription in music is the practice of notating, replicating, or otherwise committing to memory existing pieces of music.
#2. Why should I transcribe music?
Transcribing music can help you improve your listening, playing, and writing abilities. It can also help you have fun and challenge yourself with music.
#3. How do I transcribe music?
You can transcribe music by ear or using software or apps. You can also transcribe music using paper and pen. You need to listen to the piece of music and identify the notes, chords, rhythms, and other musical elements by using your ears and an instrument. And, don’t forget to write down your transcription using notation symbols or other formats.
Try FineVoice for Free
Powerful real-time voice changer for tuning your voice in gaming, streaming, and chatting. It comes with various voice & sound effects and supports creating custom voice. Get it for free.



